Introduction
In the high-stakes world of automotive manufacturing, precision, safety, and accountability aren’t just expected—they’re required. A single faulty part can lead to widespread recalls, safety hazards, and reputational damage. That’s why the industry is leaning into traceability solutions to monitor every component, process, and product across increasingly global and complex supply chains.
Ensuring Component-Level Traceability in Complex Supply Chains
Modern vehicles are made up of 30,000+ parts, often sourced from hundreds of suppliers across multiple countries. Without robust traceability:
- It becomes difficult to identify the source of defects
- Quality issues may not surface until after market release
- Recalls become expensive and time-consuming
Component-level traceability ensures every part—engine sensors, airbag inflators, brake pads, chips—is linked to a verifiable history, from manufacturing to installation.
With thermal inkjet, QR codes, RFID tags, and digital tracking systems, manufacturers can now:
- Trace parts to individual production lines and batches
- Link each vehicle to installation timestamps and operator logs
- Store metadata for lifetime diagnostics and audits
- Supporting Compliance with Automotive Safety Standards
Traceability isn’t just a best practice—it’s a regulatory necessity.
Key Standards Driving Automotive Traceability:
- ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949): Global quality management system for automotive suppliers
- UNECE WP.29 Regulations: Require secure software update traceability
- OEM-specific requirements: Like Ford’s MMOG/LE and GM’s QSB programs
These regulations mandate traceable records for defect containment, process audits, and continuous improvement.
Digital traceability helps ensure automated compliance, simplifies audits, and provides proof-of-origin documentation.
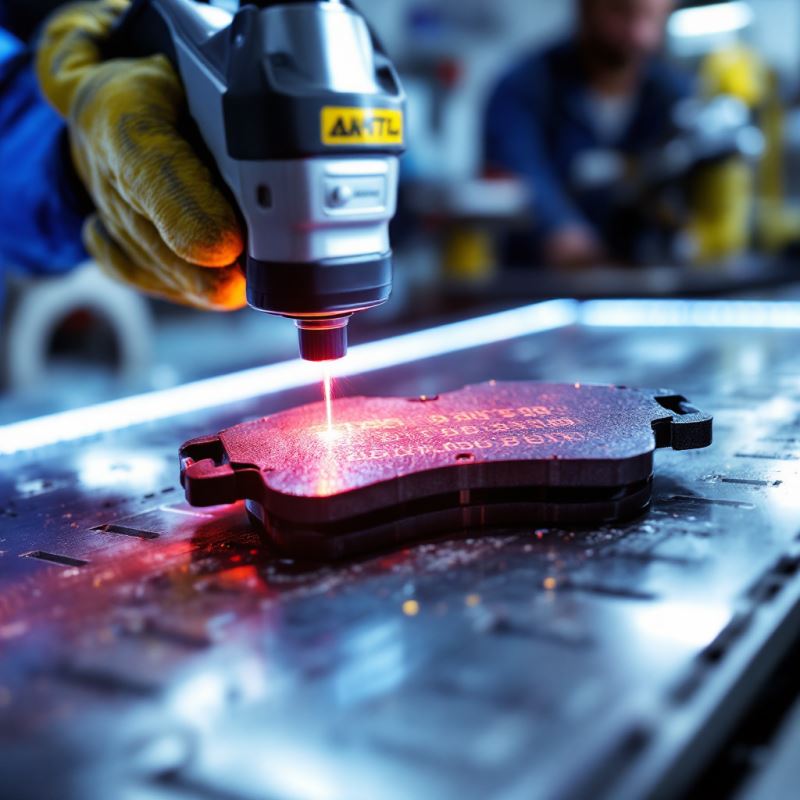 Benefits for Manufacturers
Benefits for Manufacturers
Reduced Defect Rates
Identify recurring supplier or process failures early using traceable defect data.
Efficient Recall Management
Limit recall scope to specific lots instead of entire production runs—saving millions in costs.
Faster Root Cause Analysis
Link field failures to specific component batches or software versions for faster containment.
Consumer Trust & Transparency
Prove authenticity of OEM parts and build brand loyalty through safety confidence.
 Case Studies: Automotive Brands Embracing Traceability
Case Studies: Automotive Brands Embracing Traceability
Toyota
Pioneers in lean manufacturing, Toyota uses component serialization and advanced tracking for real-time quality alerts and supplier audits.
Tesla
Uses software version tracking and vehicle telemetry to connect real-time performance to manufacturing history—enabling predictive maintenance and faster over-the-air updates.
Volkswagen
Launched a blockchain traceability project to track raw materials like cobalt, ensuring ethical sourcing and responsible recycling in EV production.
Conclusion
In a world of connected cars, global suppliers, and zero-defect expectations, traceability is the key to maintaining automotive excellence. From reducing risks and accelerating recalls to securing regulatory compliance, it drives better outcomes for manufacturers and safer vehicles for drivers.
The road to future-ready mobility starts with a transparent supply chain.